Research Techniques & Certificates
Computer Languages
-
R (main)
R is a language primarily used for statistical computing and graphics, making it popular in data science. -
Python
Python is a versatile programming language used for web development, data analysis, AI, and more. -
 SAS
SAS is used for advanced analytics, business intelligence, and data management.
SAS
SAS is used for advanced analytics, business intelligence, and data management. -
Java (entry)
Java is a general-purpose programming language that is platform-independent and widely used in web applications. -
 Linux (entry)
Linux is an open-source operating system used for various computing environments, from servers to desktops.
Linux (entry)
Linux is an open-source operating system used for various computing environments, from servers to desktops.
Statistical Modeling
-
 Linear Regression
Linear regression models the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
Linear Regression
Linear regression models the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. -
 ANOVA
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is used to compare means across multiple groups to find if they significantly differ.
ANOVA
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is used to compare means across multiple groups to find if they significantly differ. -
 Mixed Effect Models
Mixed effect models analyze data that includes both fixed and random effects, useful for complex data structures.
Mixed Effect Models
Mixed effect models analyze data that includes both fixed and random effects, useful for complex data structures. -
 Spatiotemporal Data Analysis
Spatiotemporal data analysis studies data that changes over space and time, often used in environmental studies.
Spatiotemporal Data Analysis
Spatiotemporal data analysis studies data that changes over space and time, often used in environmental studies. -
 Longitudinal Data Analysis
Longitudinal data analysis tracks data collected repeatedly over time, important for understanding changes within subjects.
Longitudinal Data Analysis
Longitudinal data analysis tracks data collected repeatedly over time, important for understanding changes within subjects. -
 Nonparametric Bayesian modeling
Nonparametric Bayesian modeling is a flexible statistical approach that allows model complexity to grow with the data by placing a prior on infinite-dimensional parameter spaces, such as distributions or functions.
Nonparametric Bayesian modeling
Nonparametric Bayesian modeling is a flexible statistical approach that allows model complexity to grow with the data by placing a prior on infinite-dimensional parameter spaces, such as distributions or functions.
Bioinformatics
-
 16S rRNA Microbiome Analysis (QIIME2)
Data preprocessing (cutadapt), ASV clustering (DADA2), alpha/beta diversity (Shannon, Weighted UniFrac), differential abundance (ANCOM-BC), taxonomy assignment (Naive Bayes classifier, Greengenes2), and phylogenetic tree construction (MAFFT + IQ-TREE), visualized with iTOL/Empress.
16S rRNA Microbiome Analysis (QIIME2)
Data preprocessing (cutadapt), ASV clustering (DADA2), alpha/beta diversity (Shannon, Weighted UniFrac), differential abundance (ANCOM-BC), taxonomy assignment (Naive Bayes classifier, Greengenes2), and phylogenetic tree construction (MAFFT + IQ-TREE), visualized with iTOL/Empress. -
 RNA-seq Analysis
Quality control (FASTQC, MultiQC), trimming (Trimmomatic), alignment (HISAT2, STAR), read counting (featureCounts), normalization (TPM, VST), and differential gene expression (DESeq2 in R/Bioconductor).
RNA-seq Analysis
Quality control (FASTQC, MultiQC), trimming (Trimmomatic), alignment (HISAT2, STAR), read counting (featureCounts), normalization (TPM, VST), and differential gene expression (DESeq2 in R/Bioconductor). -
 Statistical Analysis and Visualization
PCA, PCoA, clustering, Kruskal-Wallis, Adonis test, Mann-Whitney, ANOVA. Visualization using ggplot2, seaborn, and Emperor.
Statistical Analysis and Visualization
PCA, PCoA, clustering, Kruskal-Wallis, Adonis test, Mann-Whitney, ANOVA. Visualization using ggplot2, seaborn, and Emperor. -
 Functional Enrichment & Pathway Analysis
DAVID, KEGG (with plans to incorporate GSEA and clusterProfiler).
Functional Enrichment & Pathway Analysis
DAVID, KEGG (with plans to incorporate GSEA and clusterProfiler). -
 Computational Tools
R (tidyverse, phyloseq, DESeq2), Python, Bash scripting
Computational Tools
R (tidyverse, phyloseq, DESeq2), Python, Bash scripting
3D Technology
-
 3D Printing
3D Printing involves creating physical objects from digital models, often used in prototyping, manufacturing, and medical applications.
3D Printing
3D Printing involves creating physical objects from digital models, often used in prototyping, manufacturing, and medical applications. -
3D CAD
3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is used to create precise 3D models and designs, facilitating engineering, architecture, and manufacturing processes.
General Molecular Biology Techniques
-
 General Cloning
General cloning techniques are used to replicate DNA sequences and are fundamental for genetic manipulation and study.
General Cloning
General cloning techniques are used to replicate DNA sequences and are fundamental for genetic manipulation and study. -
 Engineering Plasmids
Engineering plasmids involves constructing vector backbones for antigen delivery or genetic modification applications.
Engineering Plasmids
Engineering plasmids involves constructing vector backbones for antigen delivery or genetic modification applications. -
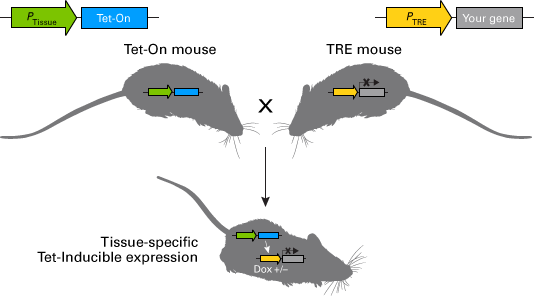 Inducible Systems
Inducible systems are designed to control gene expression, allowing targeted and timely gene activation or repression.
Inducible Systems
Inducible systems are designed to control gene expression, allowing targeted and timely gene activation or repression. -
 DNA Mutagenesis
DNA mutagenesis techniques, such as allelic exchange and transduction mutagenesis, introduce targeted mutations to study gene function.
DNA Mutagenesis
DNA mutagenesis techniques, such as allelic exchange and transduction mutagenesis, introduce targeted mutations to study gene function. -
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis, including RNA/DNA gels, SDS-PAGE, and 2D-PAGE, is used to separate biomolecules by size and charge. -
 DNA, RNA Purification
DNA and RNA purification techniques are crucial for obtaining clean samples for downstream molecular analysis.
DNA, RNA Purification
DNA and RNA purification techniques are crucial for obtaining clean samples for downstream molecular analysis. -
 LPS profiling
LPS profiling is the analysis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in bacterial cell membranes to understand their structure, composition, and role in immune response and pathogenicity.
LPS profiling
LPS profiling is the analysis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in bacterial cell membranes to understand their structure, composition, and role in immune response and pathogenicity. -
qRT-PCR
qRT-PCR is a quantitative PCR technique used to measure RNA levels, allowing gene expression analysis. -
Protein Purification
Protein purification isolates specific proteins for functional and structural studies. -
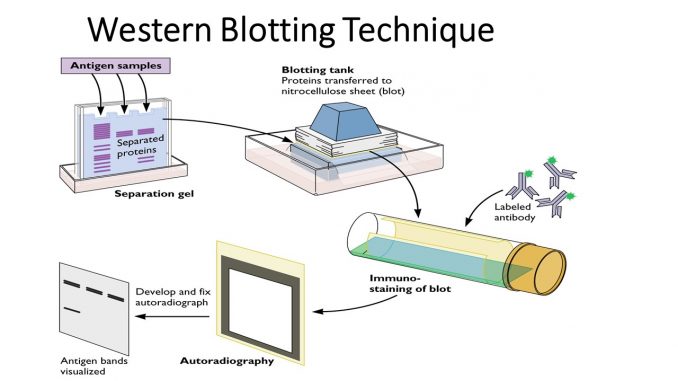 Western Blotting
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample using antibodies.
Western Blotting
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample using antibodies. -
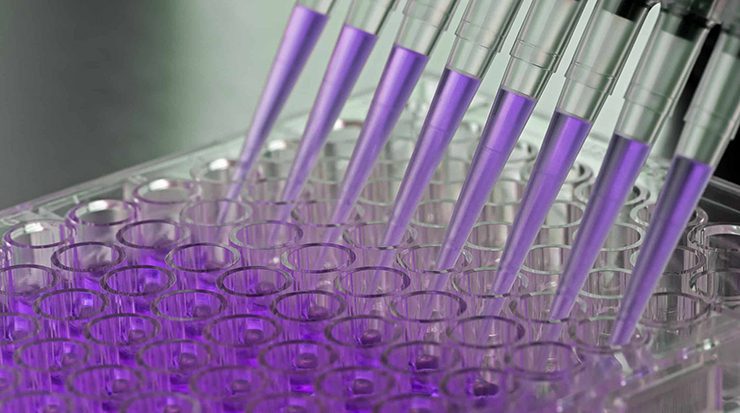 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA is a plate-based assay used to detect and quantify substances such as proteins, antibodies, and hormones.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA is a plate-based assay used to detect and quantify substances such as proteins, antibodies, and hormones. -
 Bacteria Cell Fractionation and Protein Profiling
Bacteria cell fractionation and protein profiling involve separating bacterial cellular components to analyze and identify proteins, providing insights into their functions and roles within the cell.
Bacteria Cell Fractionation and Protein Profiling
Bacteria cell fractionation and protein profiling involve separating bacterial cellular components to analyze and identify proteins, providing insights into their functions and roles within the cell. -
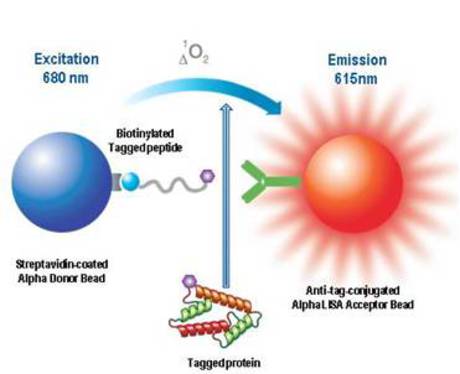 Protein Interaction Assays
Protein interaction assays investigate interactions between proteins, revealing signaling and structural pathways.
Protein Interaction Assays
Protein interaction assays investigate interactions between proteins, revealing signaling and structural pathways. -
 Beta-Galactosidase Assays
Beta-galactosidase assays measure enzyme activity, often used in gene expression studies.
Beta-Galactosidase Assays
Beta-galactosidase assays measure enzyme activity, often used in gene expression studies.
Bacterial Phage Techniques
-
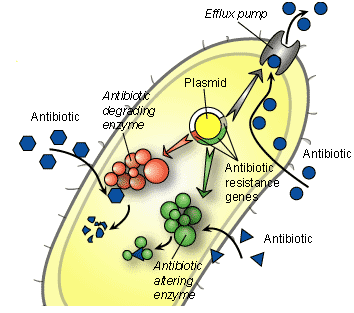 General Maintenance
General maintenance of bacterial phages includes processes like expansion, storage, and titration to ensure viability and usability.
General Maintenance
General maintenance of bacterial phages includes processes like expansion, storage, and titration to ensure viability and usability. -
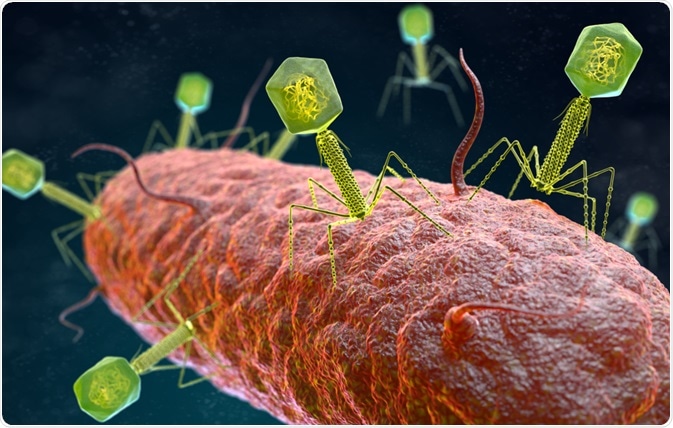 Transduction
Transduction is a method used to introduce genetic material into bacterial cells via bacteriophages, aiding in genetic studies and manipulation.
Transduction
Transduction is a method used to introduce genetic material into bacterial cells via bacteriophages, aiding in genetic studies and manipulation.
General Microbiology Techniques
-
 Standard Bacterial Cell Culture
Standard bacterial cell culture techniques involve growing bacteria in controlled conditions to study their behavior, characteristics, and applications.
Standard Bacterial Cell Culture
Standard bacterial cell culture techniques involve growing bacteria in controlled conditions to study their behavior, characteristics, and applications. -
Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Species
Techniques for isolating and identifying bacterial species are essential in microbiology for species characterization and study. -
Various Biochemical Testing
Biochemical tests are conducted to assess metabolic and chemical properties of bacteria, aiding in identification and classification. -
 Culture using dynamic NASA-designed Rotating Wall Vessel (RWV) bioreactors
The Rotating Wall Vessel (RWV) bioreactor, designed by NASA, provides a dynamic culture environment that simulates microgravity for advanced bacterial studies.
Culture using dynamic NASA-designed Rotating Wall Vessel (RWV) bioreactors
The Rotating Wall Vessel (RWV) bioreactor, designed by NASA, provides a dynamic culture environment that simulates microgravity for advanced bacterial studies.
Cell and Tissue Culture Techniques
-
Standard monolayer cell culture techniques (including intestinal epithelial cells, monocytes, macrophages)
Standard monolayer cell culture techniques are used for cultivating cells such as intestinal epithelial cells, monocytes, and macrophages in a two-dimensional layer. -
Three-dimensional (3-D) organotypic intestinal cell culture using RWV bioreactors
Three-dimensional (3D) organotypic intestinal cell cultures are developed using RWV bioreactors, providing a more physiologically relevant model for cell studies. -
 3-D human intestinal epithelial co-cultures containing human macrophages
3D human intestinal epithelial co-cultures integrate human macrophages, creating a complex model to study host-microbe interactions.
3-D human intestinal epithelial co-cultures containing human macrophages
3D human intestinal epithelial co-cultures integrate human macrophages, creating a complex model to study host-microbe interactions. -
Bacterial infection studies (gentamicin protection assay)
Bacterial infection studies, such as the gentamicin protection assay, are used to investigate bacterial invasion and replication within host cells. -
 Tissue Regeneration
Tissue regeneration techniques explore the ability of cells and tissues to repair and renew, essential in regenerative medicine research.
Tissue Regeneration
Tissue regeneration techniques explore the ability of cells and tissues to repair and renew, essential in regenerative medicine research.
Caenorhabditis elegans Techniques
-
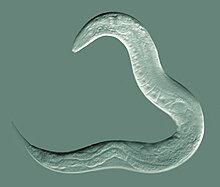 General Maintenance
General maintenance of *C. elegans* includes feeding, freezing, and recovery processes to ensure healthy and viable populations.
General Maintenance
General maintenance of *C. elegans* includes feeding, freezing, and recovery processes to ensure healthy and viable populations. -
 Egg and Larvae Preparation
Egg preparation and larvae staging (L1 and L4) are essential for developmental studies and controlled experimental setups.
Egg and Larvae Preparation
Egg preparation and larvae staging (L1 and L4) are essential for developmental studies and controlled experimental setups. -
 Infection Study and TD50
Infection studies in *C. elegans*, including TD50 determination, are used to analyze pathogen interactions and host response.
Infection Study and TD50
Infection studies in *C. elegans*, including TD50 determination, are used to analyze pathogen interactions and host response.
Microscopy and Staining Techniques
-
 Light Microscopy
Light microscopy is a basic technique used to visualize cells and tissues with the aid of visible light.
Light Microscopy
Light microscopy is a basic technique used to visualize cells and tissues with the aid of visible light. -
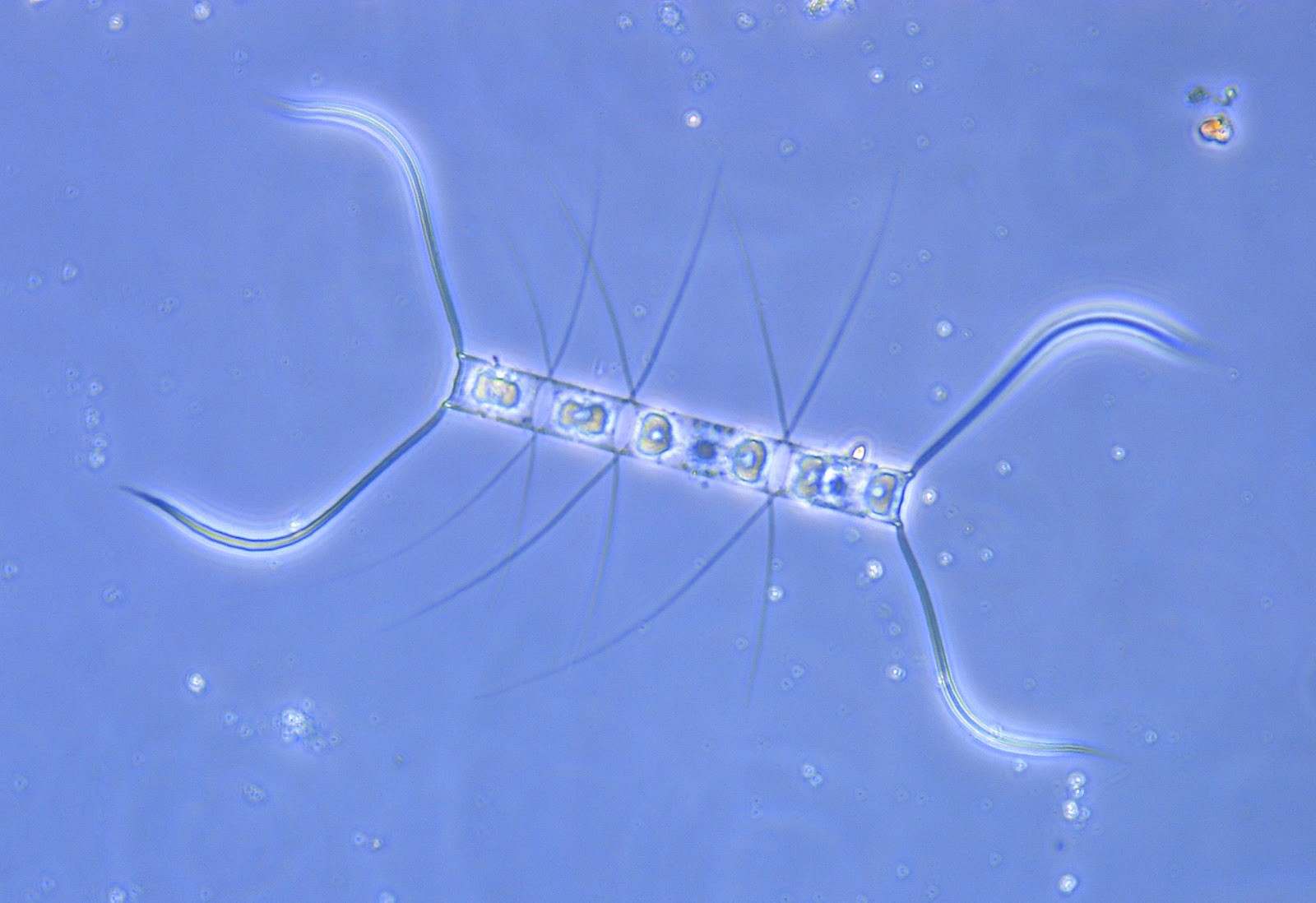 Phase Contrast Microscopy
Phase contrast microscopy enhances contrast in transparent specimens, making it ideal for observing live cells.
Phase Contrast Microscopy
Phase contrast microscopy enhances contrast in transparent specimens, making it ideal for observing live cells. -
 Epi-Fluorescent Microscopy
Epi-fluorescent microscopy uses fluorescence to illuminate specimens, allowing visualization of specific cellular components.
Epi-Fluorescent Microscopy
Epi-fluorescent microscopy uses fluorescence to illuminate specimens, allowing visualization of specific cellular components. -
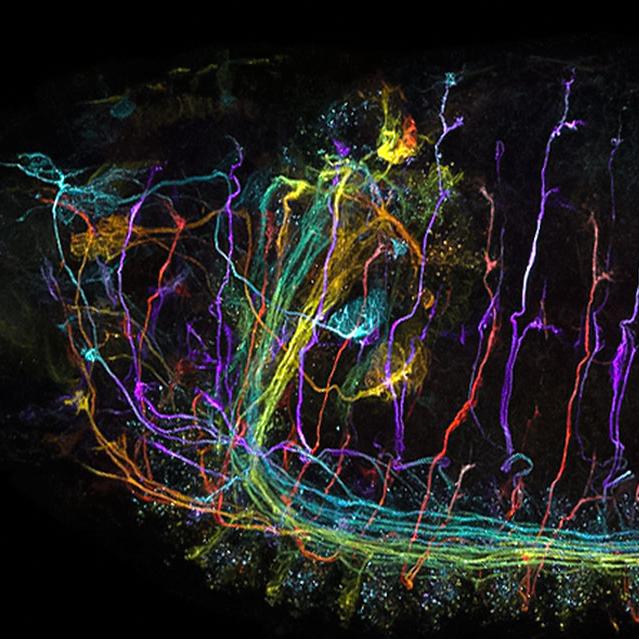 Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (4 lasers to white laser, multiple channels)
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy uses multiple laser channels, including options from 4 lasers to a white laser, to produce high-resolution, 3D images of specimens by selectively illuminating specific depths and capturing detailed optical sections.
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (4 lasers to white laser, multiple channels)
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy uses multiple laser channels, including options from 4 lasers to a white laser, to produce high-resolution, 3D images of specimens by selectively illuminating specific depths and capturing detailed optical sections. -
 Expertise in a wide range of chemical staining techniques for microscopic imaging of both bacterial and mammalian cells, including immunohistochemical profiling and biofilm staining
Expertise in various chemical staining techniques for bacterial and mammalian cells, including immunohistochemistry and biofilm staining.
Expertise in a wide range of chemical staining techniques for microscopic imaging of both bacterial and mammalian cells, including immunohistochemical profiling and biofilm staining
Expertise in various chemical staining techniques for bacterial and mammalian cells, including immunohistochemistry and biofilm staining. -
 SEM and TEM (not expert)
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) are advanced techniques for high-resolution imaging of cellular structures.
SEM and TEM (not expert)
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) are advanced techniques for high-resolution imaging of cellular structures.
Animal Studies Techniques
-
 Generating Polyclonal Antibodies
Techniques for generating polyclonal antibodies using small laboratory animals such as rabbits, mice, and chickens.
Generating Polyclonal Antibodies
Techniques for generating polyclonal antibodies using small laboratory animals such as rabbits, mice, and chickens. -
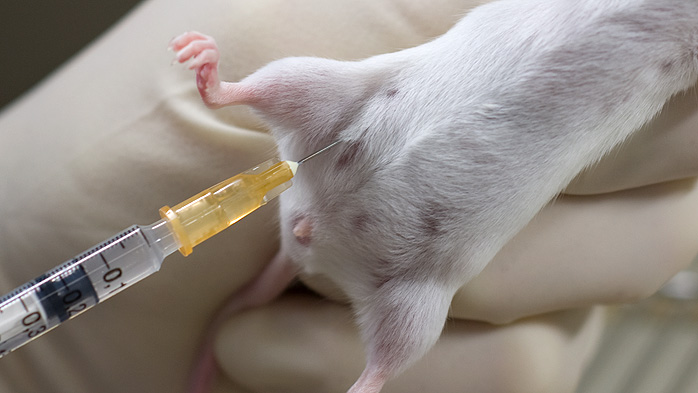 Oral, Intraperitoneal, and Intradermal Administration
Methods for administering substances orally, intraperitoneally, or intradermally to laboratory animals.
Oral, Intraperitoneal, and Intradermal Administration
Methods for administering substances orally, intraperitoneally, or intradermally to laboratory animals. -
 Animal Infections and LD50 Studies
Techniques for studying animal infections and determining the lethal dose 50% (LD50) in experimental animals.
Animal Infections and LD50 Studies
Techniques for studying animal infections and determining the lethal dose 50% (LD50) in experimental animals. -
 Tissue Dissections in Mice and Chickens
Procedures for dissecting tissues in mice and chickens to study various biological processes and diseases.
Tissue Dissections in Mice and Chickens
Procedures for dissecting tissues in mice and chickens to study various biological processes and diseases. -
 Examination of Mouse and Chicken Organs
Examination of Mouse and Chicken Organs
-
Isolation and Quantitation of Microorganisms from Animal Tissues and Organs
-
 Cardiac Puncture
Cardiac puncture is a technique used for obtaining blood samples from laboratory animals for analysis.
Cardiac Puncture
Cardiac puncture is a technique used for obtaining blood samples from laboratory animals for analysis.
Biofilm Study Techniques
-
Standard Biofilm Culture
Standard biofilm culture techniques are used to grow single or mixed-species biofilms under controlled conditions. -
 EPS Detection
Techniques for detecting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and other extracellular compounds in biofilms.
EPS Detection
Techniques for detecting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and other extracellular compounds in biofilms. -
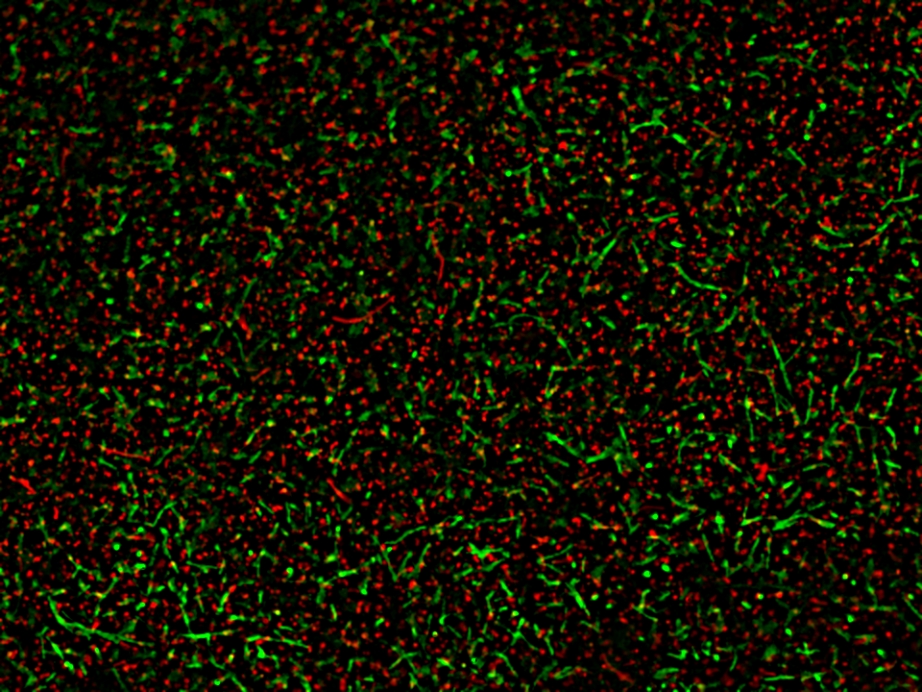 Live/Dead Staining
Live/dead staining techniques are used to assess the viability of cells within a biofilm, distinguishing live cells from dead ones.
Live/Dead Staining
Live/dead staining techniques are used to assess the viability of cells within a biofilm, distinguishing live cells from dead ones.
Space Life Science Techniques
-
Spaceflight Hardware for ISS Experiments
Utilization of various spaceflight hardware to conduct biological experiments aboard the International Space Station (ISS). -
 Spaceflight-Analogue Cell Culture Systems
Use of spaceflight-analogue cell culture systems to simulate microgravity and other space conditions for biological studies on Earth.
Spaceflight-Analogue Cell Culture Systems
Use of spaceflight-analogue cell culture systems to simulate microgravity and other space conditions for biological studies on Earth. -
 Spaceflight Experiment aboard ISS
Spaceflight Experiment aboard ISS
Development of various selective or selective/deferential media
-
 Developing Selective Media
Developing selective media involves creating a growth medium that supports the growth of specific microorganisms while inhibiting the growth of others.
Developing Selective Media
Developing selective media involves creating a growth medium that supports the growth of specific microorganisms while inhibiting the growth of others. -
 Developing Differential/Selective Media
Developing differential/selective media involves formulating a growth medium that not only supports the growth of specific microorganisms while inhibiting others but also allows for the differentiation between microbial types based on their biochemical properties.
Developing Differential/Selective Media
Developing differential/selective media involves formulating a growth medium that not only supports the growth of specific microorganisms while inhibiting others but also allows for the differentiation between microbial types based on their biochemical properties.
Languages
-
English
Proficient in English, used for communication, academic writing, and professional collaboration. -
 Korean
Fluent in Korean, used for native communication, cultural understanding, and bilingual support.
Korean
Fluent in Korean, used for native communication, cultural understanding, and bilingual support.